
The present perfect tense is one of the most common English verb tenses, and it’s used in several different ways. This lesson will teach you everything you ever wanted to know about the present perfect – try the four quizzes with grammar exercises in each section!


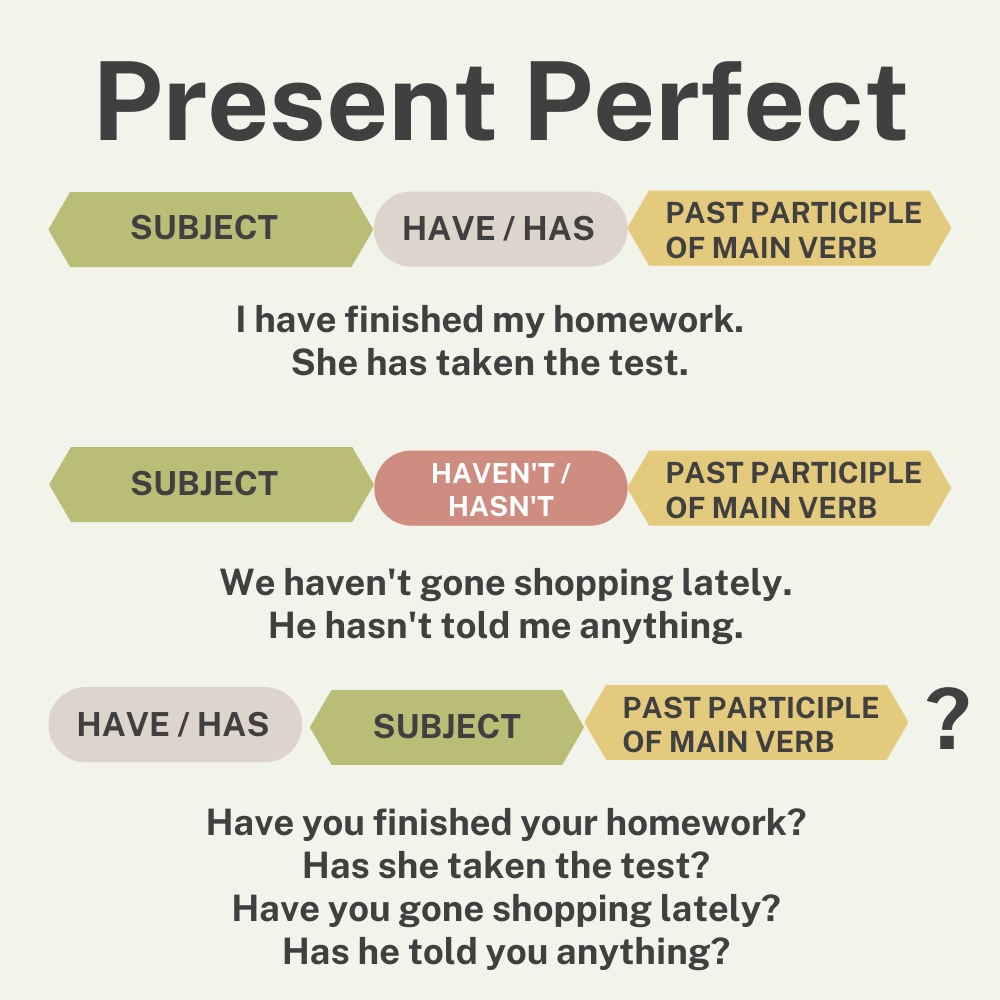
The present perfect is formed by subject + have/has + past participle of the main verb, for example:
We use the present perfect for unfinished time (a period of time that continues to the present moment), differently from the simple past tense which describes finished time:
We also use the present perfect tense for unspecified time (when we don’t know or don’t say exactly when), differently from the simple past tense which describes specific time:
 the present perfect for unfinished time and unspecified time" width="300" height="226" />
the present perfect for unfinished time and unspecified time" width="300" height="226" />
| SUBJECT | HAVE / HAS | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| I / you / we / they | have | written |
| he / she / it | has | written |
Note: In spoken English, it’s common to use the contraction for the auxiliary verb have or has:
In this case, he’s, she’s, Barbara’s, etc. mean he has, she has, and Barbara has, not he is, she is, or Barbara is.
| SUBJECT | HAVEN’T / HASN’T | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| I / you / we / they | haven’t | seen |
| he / she / it | hasn’t | seen |
| HAVE / HAS | SUBJECT | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| Have | I / you / we / they | finished? |
| Has | he / she / it | finished? |
How to answer present perfect questions:
We can create a “short answer” using the auxiliary verb have/has, or their negative forms haven’t/hasn’t:

In the present perfect, it’s possible to say “have had” and “has had” when “have” is BOTH the auxiliary verb (helping verb) AND the main verb in the sentence, for example:
 the present perfect" width="500" height="500" />
the present perfect" width="500" height="500" />
The past participle form of the verb describes a completed action or state.
For regular verbs, the past participle is the same as the past simple tense:
This is also the case for many irregular verbs:
However, some irregular verbs’ past participles are different from their simple past form:
Many of these irregular past participles end in –n:
| Infinitive | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| be | was / were | been |
| break | broke | broken |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| do | did | done |
| drive | drove | driven |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| know | knew | known |
| see | saw | seen |
| show | showed | shown |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| take | took | taken |
| wear | wore | worn |
| write | wrote | written |
Other irregular past participles have a change in the vowel:
| Infinitive | Simple Past | Past Participle |
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| come | came | come |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| ring | rang | rung |
| run | ran | run |
| sing | sang | sung |
| swim | swam | swum |
Congratulations - you have completed Present Perfect Quiz. You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
The correct sentence is: "Gary has known Darla for a long time." or: "Gary's known Darla for a long time."
Question 6 They already given me the money. Question 6 Explanation: The correct sentence is: "They've already given me the money." Question 7 We've recently wrote a book. Question 7 Explanation: The correct sentence is: "We've recently written a book." Question 8 I've lived in Orlando for three years. Question 9 Have you ever drived a Ferrari? Question 9 Explanation: The correct sentence is "Have you ever driven a Ferrari?" Question 10 Has you ever met my brother? Question 10 Explanation: The correct sentence is: "Have you ever met my brother?" Question 11 She's been to Berlin twice. Question 12 Has he ever eaten Brazilian food? Question 13 No, they hasn't eaten lunch yet. Question 13 Explanation: The correct sentence is: "No, they haven't eaten lunch yet." Question 14 I haven't read today's newspaper yet. Question 14 Explanation: the past participle of "read" is "read" - but it's pronounced like "red" Question 15 Have you heard the new song by Adele?Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect. Get Results
There are 15 questions to complete. You have completed Your score is Partial-Credit You have not finished your quiz. If you leave this page, your progress will be lost. Correct Answer You Selected Not Attempted Final Score on Quiz Attempted Questions Correct Attempted Questions Wrong Questions Not Attempted Total Questions on Quiz Question Details Time allowed Answer Choice(s) Selected Question Text Need more practice! Keep trying!The present perfect is used with ever and never to talk about actions done at any time in a person’s life, or at any time in history until now.
Use ever in questions only – NOT in statements.
Use never in statements – but only with have/has, not with haven’t/hasn’t:
The words already, yet, recently, lately, and just all refer to a recent and non-specific time period. (A specific time would be “yesterday” or “three hours ago” or last Friday,” and in these cases we would use the simple past).
Already can be used in positive statements and questions.
Note: Already can go in between “have/has” and the past participle (as in the first two examples) or at the end of the sentence.
Yet can be used in negative statements and questions.
Note: Yet usually goes at the end of the sentence or phrase.
Recently and lately can be used in positive statements, negative statements, or questions:
Recently
Lately
Just (usually means very recent) is typically only used in positive statements and questions:
Spoken American English often uses the simple past with already, yet, and just:
Congratulations - you have completed Quiz: Present Perfect with ever, never, already, recently, lately, and just. You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect. Get Results
There are 7 questions to complete. You have completed Your score is Partial-Credit You have not finished your quiz. If you leave this page, your progress will be lost. Correct Answer You Selected Not Attempted Final Score on Quiz Attempted Questions Correct Attempted Questions Wrong Questions Not Attempted Total Questions on Quiz Question Details Time allowed Answer Choice(s) Selected Question Text Need more practice! Keep trying!The present perfect is also used with for and since to talk about actions that began in the past and continue to the present.
Since is used with a point in time, and means “from that point in time until the present.” Use since with dates (2011, January, Tuesday, etc.), times (6:15, noon, this morning, etc.), and past events (I was a child, he graduated from college, etc).
Since is always used with the present perfect, and not the simple past:
For is used with a time period, and means “for that period of time until the present.” Use for with time periods of any length (five seconds, eight hours, two days, six weeks, nine months, ten years, a decade, centuries, etc.)
Be careful with for, because using the present perfect or the simple past can change the meaning:
Congratulations - you have completed Quiz: Present perfect with FOR and SINCE. You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%